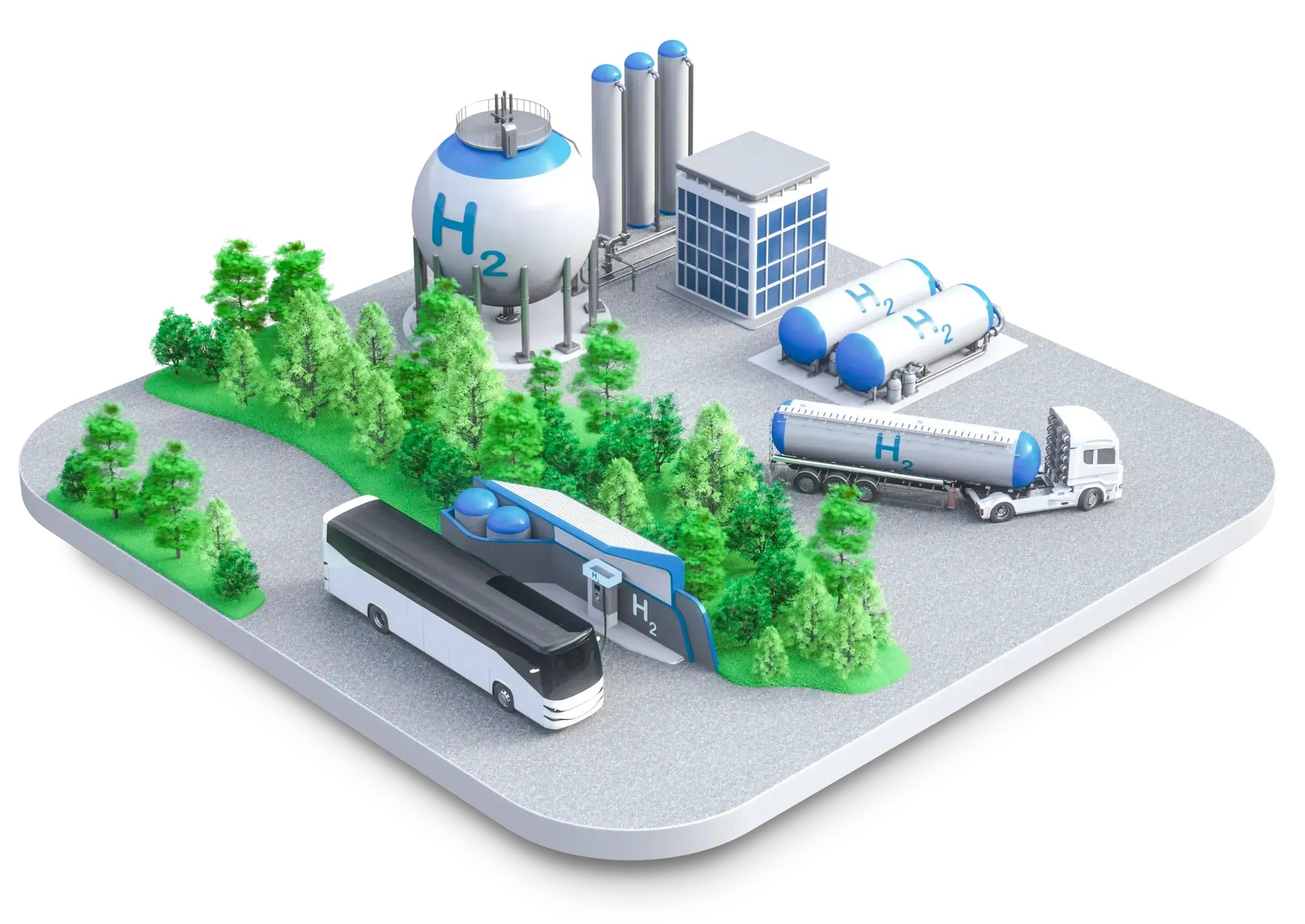
Seals for hydrogen distribution and storage have to do more than just close a connection. In distribution and storage stages, small-molecule hydrogen, large pressure differentials, temperature fluctuations and strict safety standards come together. Therefore, it comes down to low permeation, a stable compression set and predictable behaviour during cyclic operation. These seals truly perform only when they remain gas-tight after long-term use, respect tolerances and allow repeatable assembly. We combine product forms (O-rings, X-rings, static gaskets, dynamic seals and PTFE back-up rings) with compounds (EPDM, FKM, FFKM, HNBR/AFLAS, PTFE/PEEK) that match the medium, temperature, pressure differential and desired service life. In this way, seals for hydrogen distribution and storage become a lever for safety, efficiency and predictable operating costs.
Leakage in hydrogen distribution and storage is both a safety risk and a cost factor. Seals with low permeation limit microleakage that could otherwise go unnoticed due to the small molecular size. Seals for hydrogen distribution and storage keep flanges, valves, couplings and measurement points gas-tight, even after thermal cycles and vibration. In static joints it comes down to uniform compression distribution, correct bolt preload and suitable surface roughness; in dynamic parts, friction and heat generation come into play.
AED/RGD-resistant compounds reduce the risk of internal damage due to rapid decompression in gas service, while PTFE back-up rings help prevent extrusion at large pressure differentials. Thus, low-permeation seals reduce both emissions and safety incidents, and keep the installation compliant with internal HSE requirements and external audits.
Unplanned stops, purge actions and restarts directly impact reliability and budget. Seals for hydrogen distribution and storage extend maintenance intervals by ensuring dimensional stability and consistent compression. In high-pressure interfaces, O-rings with PTFE back-up rings remain tight at large pressure differentials; in flanges, the right hardness delivers stable leak-tightness. By standardising on ISO 3601 groove dimensions and on a limited number of compounds, assembly times become shorter and inventory management predictable. Hydrogen storage seals and hydrogen distribution seals that combine demonstrably low permeation and robust AED properties reduce failure costs, minimise product loss and improve Total Cost of Ownership over the full lifecycle.
We supply a complete package focused on distribution and storage: O-rings and X-rings (static and dynamic), static gaskets for flanges and inspection hatches, valve and fitting seals (seat/stem), coupling and quick-connect O-rings, plus dynamic sets with guidance for critical moving parts. PTFE back-up rings and PEEK elements increase extrusion resistance when gap width or pressure differential increases. Seals for hydrogen distribution and storage must allow repeatable assembly, compress uniformly and show predictable behaviour under repeated loading. With clear guidelines around dimensions, torque and surface specifications, tolerances are controlled and leak-tightness remains stable, even when ambient temperature and load vary.
Material selection determines compatibility, service life and safety. EPDM is often logical for water/alkali and utilities; FKM performs strongly in the 150–200 °C range and with various chemicals; FFKM pays off for extreme chemistry and heat. HNBR or AFLAS are suitable when sour service or gas mixes are involved; PTFE/PEEK provides low friction and dimensional stability and serves as a back-up at large pressure differentials. Seals for hydrogen distribution and storage benefit from low-permeation seals and compounds with a low compression set, so that the sealing pressure is maintained. ISO 3601 groove dimensions ensure comparable assembly conditions between lines and locations. In gas service, an AED/RGD-resistant material choice is often sensible; test reports for permeation, compression set and RGD behaviour substantiate selection and audits.
In manifolds, tube trailers, transmission pipelines and refuelling stations, the combination of large pressure differentials, temperature swings and frequent (dis)connections is the norm. Seals for hydrogen distribution and storage must keep extrusion under control, absorb tolerances and remain tight even after many cycles. PTFE back-up rings limit gap extrusion and stabilise sealing pressure; AED/RGD-resistant O-rings reduce risks during rapid pressure drops in gas service. In couplings and quick-connects, well-chosen hardnesses compensate for dimensional variation and lubrication condition, keeping handling safe and smooth. Hydrogen distribution seals tuned to ISO 3601 groove dimensions shorten changeover times and reduce error risk in the field. In this way, seals for hydrogen distribution and storage deliver immediate returns in places where every minute counts.
Storage tanks and vessels require stable flange gaskets, inspection hatch seals and valve seals that remain leak-free during temperature fluctuations and standstill. Seals for hydrogen distribution and storage with low permeation limit “sweating” and product loss; a low compression set maintains sealing pressure over longer intervals. In fittings, from seat and stem seals to instrumentation interfaces, repeatable assembly is crucial. ISO 3601 groove dimensions, the right hardness and consistent surface specifications ensure uniform compression and predictable results.
Where sour service, traces of CO/CO₂ or other contaminants are present, material choices such as HNBR/AFLAS help secure compatibility and service life. Ultimately, seals for hydrogen distribution and storage make the difference between planned maintenance and reactive repairs, between controlled emissions and costly downtime.
Roughly: EPDM for water/alkali, FKM for 150–200 °C and chemical exposure, FFKM for extreme chemistry/heat. HNBR/AFLAS for sour service; PTFE/PEEK for low friction and back-ups in high-pressure connections.
In cases of large pressure differentials, larger gap widths or higher temperatures to prevent extrusion. They stabilise sealing pressure and increase service life in valves, couplings and flange connections.
RGD is damage caused by rapid gas decompression; AED/RGD-resistant compounds provide extra assurance. In hydrogen distribution and storage with pressure swings, this reduces the chance of internal cracking and loss of leak-tightness.
Work with ISO 3601 groove dimensions, define tolerances and surface roughness, and calibrate torque/bolt preload. This gives you repeatable compression and predictable performance across installations and shifts.
In most distribution and storage applications, yes: they limit microleakage and product loss. Choose the permeation class suited to pressure, temperature and operating duration so that seals for hydrogen distribution and storage remain gas-tight even after a long time.